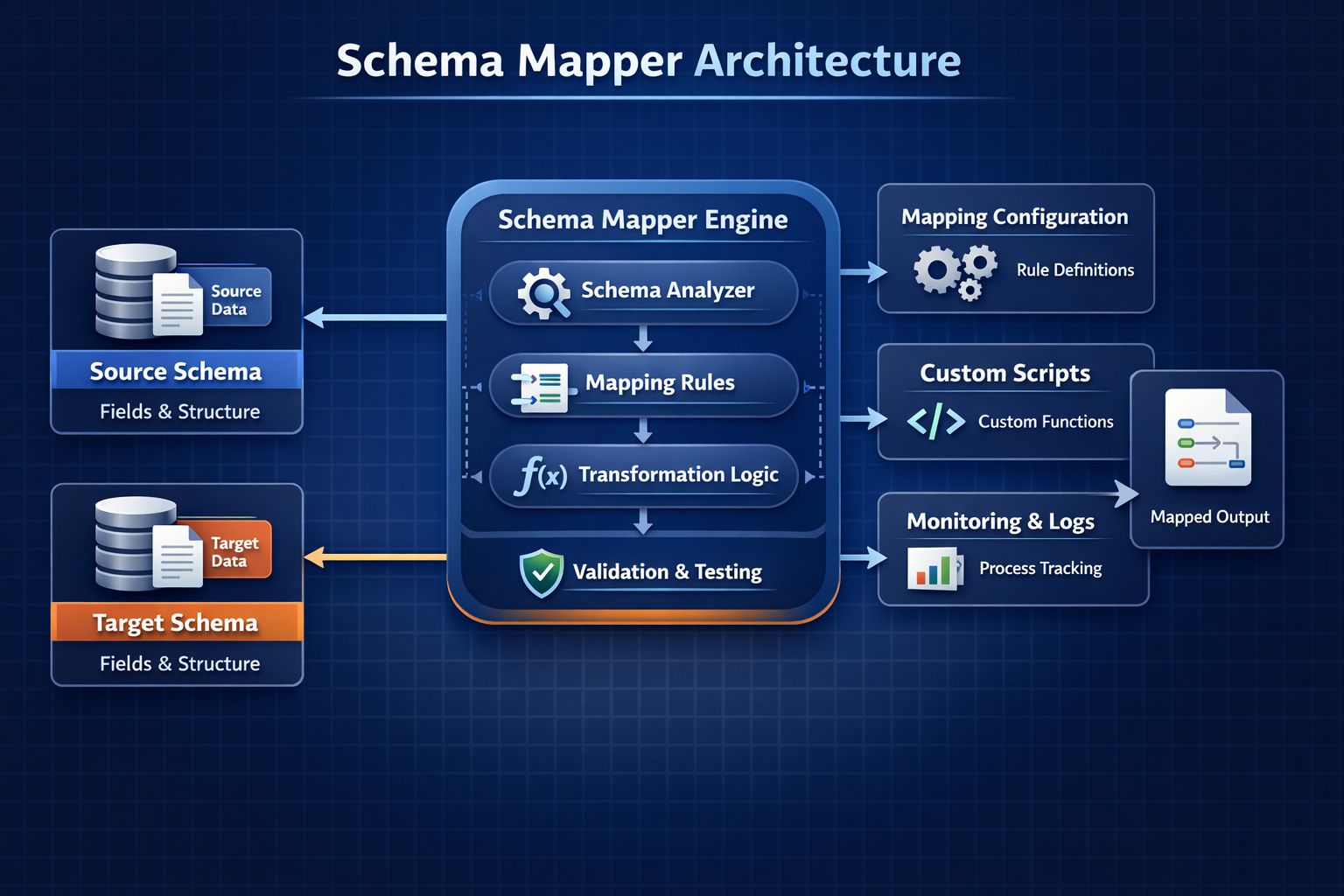
Quick Start
From DataFrame to production database in one unified API
Unified Connection Layer (NEW!)
from schema_mapper import infer_canonical_schema
from schema_mapper.connections import ConnectionFactory, ConnectionConfig
import pandas as pd
# 1. Infer schema from DataFrame
df = pd.read_csv('events.csv')
schema = infer_canonical_schema(
df,
table_name='events',
dataset_name='analytics',
partition_columns=['event_date'],
cluster_columns=['user_id', 'event_type']
)
# 2. Add metadata (governance ready!)
schema.description = "User interaction events from web and mobile"
schema.owner = "analytics-team"
schema.columns[0].description = "Unique event identifier"
schema.columns[0].pii = False # PII governance flag
# 3. Connect to ANY database with unified API
config = ConnectionConfig('config/connections.yaml')
with ConnectionFactory.get_connection('bigquery', config) as conn:
# Test connection
if conn.test_connection():
print("Connected!")
# Create table from canonical schema
conn.create_table_from_schema(schema, if_not_exists=True)
# Load data
conn.load_dataframe(df, schema.table_name, schema.dataset_name)
# Switch platforms? Just change 'bigquery' to 'snowflake'!
# Same code works for all 5 platforms.
YAML-Driven Schemas with Metadata
from schema_mapper import load_schema_from_yaml, save_schema_to_yaml
# Save schema + metadata to YAML (version control this!)
save_schema_to_yaml(schema, 'schemas/events.yaml')
# Load schema in deployment pipeline
schema = load_schema_from_yaml('schemas/events.yaml')
# Validate metadata completeness (CI/CD ready)
errors = schema.validate_metadata(
required_table_fields=['description', 'owner'],
required_column_fields=['description', 'pii']
)
if errors:
raise ValueError(f"Metadata validation failed: {errors}")
# Export data dictionary (Markdown, CSV, JSON)
markdown = schema.export_data_dictionary('markdown')
with open('docs/events_dictionary.md', 'w') as f:
f.write(markdown)
# Result: Schema + metadata as single source of truth!
Complete Pipeline (Profile → Clean → Validate → Load)
from schema_mapper import Profiler, PreProcessor, SchemaMapper
import pandas as pd
# Load your data
df = pd.read_csv('customer_data.csv')
# Step 1: PROFILE - Understand your data
profiler = Profiler(df)
quality = profiler.assess_quality()
print(f"Quality Score: {quality['overall_score']}/100")
anomalies = profiler.detect_anomalies()
print(f"Found {len(anomalies)} columns with outliers")
# Visualize (no matplotlib imports needed!)
profiler.plot_distributions()
profiler.plot_correlations()
# Step 2: CLEAN - Preprocess and standardize
preprocessor = PreProcessor(df)
df_clean = (preprocessor
.fix_whitespace()
.standardize_column_names()
.standardize_dates(['created_at'])
.validate_emails('email', fix=True)
.remove_duplicates(subset=['user_id'])
.handle_missing_values(strategy='auto')
.apply()
)
# Step 3: GENERATE - Create optimized schema
mapper = SchemaMapper('bigquery')
schema, mapping = mapper.generate_schema(df_clean)
ddl = mapper.generate_ddl(df_clean, 'customers', 'analytics', 'my-project')
# Step 4: EXPORT - Save artifacts
df_clean.to_csv('customers_clean.csv', index=False)
with open('schema.json', 'w') as f:
f.write(mapper.generate_bigquery_schema_json(df_clean))
with open('create_table.sql', 'w') as f:
f.write(ddl)
print("Ready to load!")
One-Line ETL Preparation
from schema_mapper import prepare_for_load
import pandas as pd
# Load your messy data
df = pd.read_csv('messy_data.csv')
# Prepare for ANY platform in one line!
df_clean, schema, issues = prepare_for_load(
df,
target_type='bigquery', # or 'snowflake', 'redshift', 'sqlserver', 'postgresql'
)
# Check for issues
if not issues['errors']:
print(f"SUCCESS: {len(schema)} columns prepared and ready to load!")
else:
print("ERROR: Fix these errors:", issues['errors'])
ML Feature Engineering (NEW in v1.3.0!)
from schema_mapper import Profiler, PreProcessor
import pandas as pd
# Load your data
df = pd.read_csv('customer_churn.csv')
# 1. ANALYZE: Find most important features for your target
profiler = Profiler(df, name='churn_analysis')
# Automatic target correlation analysis (handles categorical targets!)
feature_importance = profiler.analyze_target_correlation(
target_column='churn', # Works with both categorical and numeric targets
method='pearson',
top_n=15
)
print(feature_importance)
# feature correlation abs_correlation
# 0 tenure_months -0.352 0.352
# 1 monthly_charges 0.298 0.298
# 2 support_tickets 0.245 0.245
# 2. VISUALIZE: Feature importance chart (one line!)
fig = profiler.plot_target_correlation('churn', top_n=15)
fig.savefig('feature_importance.png', dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
# 3. PREPROCESS: Auto-detect and encode categorical columns
preprocessor = PreProcessor(df)
preprocessor.auto_encode_categorical(
exclude_columns=['churn', 'customer_id'], # Don't encode target/ID
max_categories=10, # Only encode low-cardinality
drop_first=True # Avoid multicollinearity
)
# ML-ready dataset!
print(f"Ready for ML: {preprocessor.df.shape}")
# Original: (10000, 15) → After encoding: (10000, 45)
Database Discovery & Introspection (NEW in v1.3.0!)
from schema_mapper.connections import ConnectionFactory, ConnectionConfig
# Connect to any database
config = ConnectionConfig('config/connections.yaml')
with ConnectionFactory.get_connection('bigquery', config) as conn:
# 1. Get all tables with metadata (DataFrames everywhere!)
tables = conn.get_tables(schema_name='analytics')
print(tables)
# table_name table_type num_rows size_mb created
# 0 users TABLE 150000 245.5 2024-01-01 10:00:00
# 1 events TABLE 5000000 8920.3 2024-01-05 11:00:00
# Find large tables
large_tables = tables[tables['size_mb'] > 1000]
# 2. Get all schemas/datasets
datasets = conn.get_datasets()
print(f"Found {len(datasets)} datasets")
# 3. Get complete warehouse structure
tree = conn.get_database_tree(format='dataframe')
tree.to_csv('warehouse_inventory.csv')
# Or as JSON for documentation
tree_dict = conn.get_database_tree(format='dict')
# Same code works for all 5 platforms!
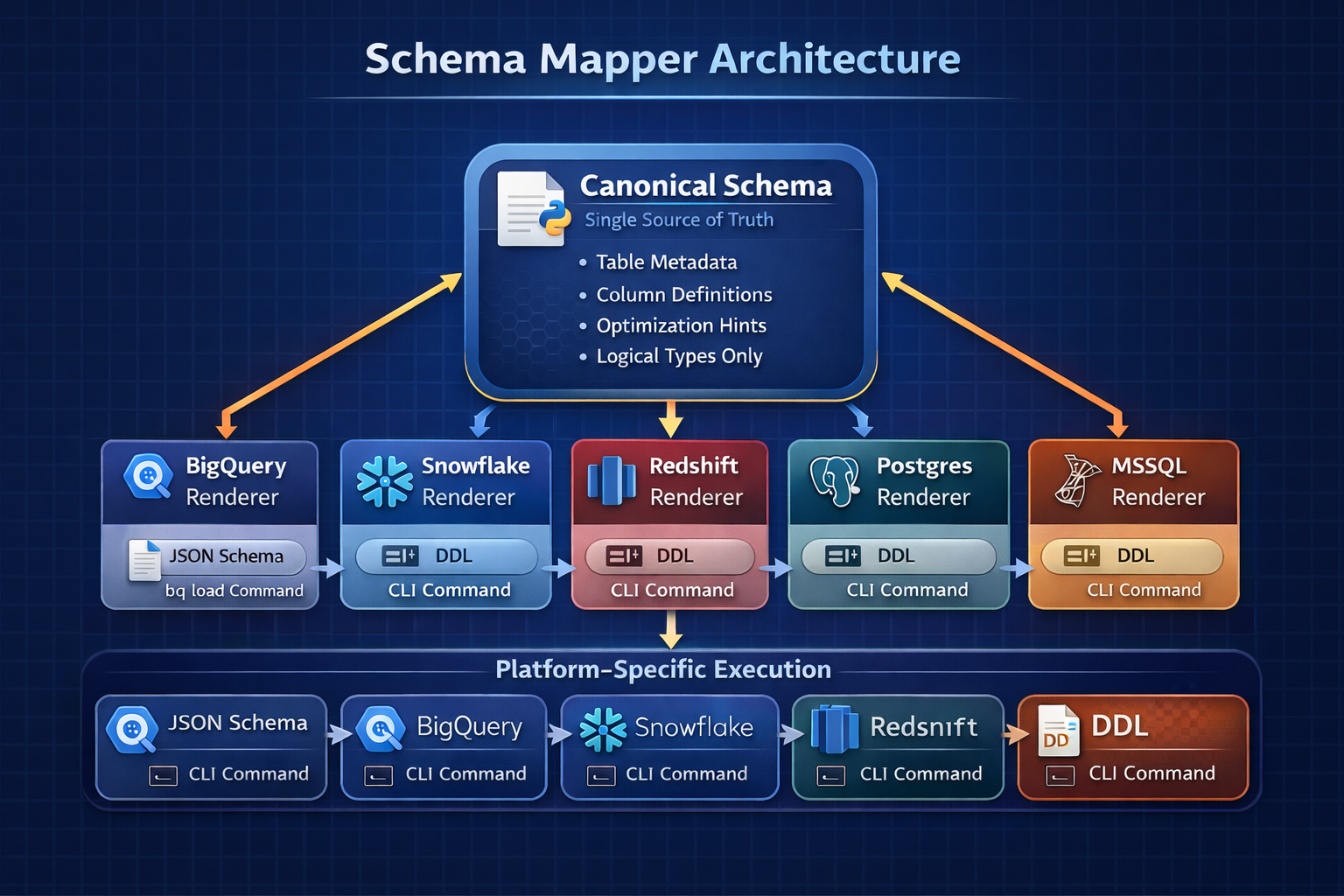
Canonical Schema → Multi-Platform
from schema_mapper.canonical import infer_canonical_schema
from schema_mapper.renderers import RendererFactory
# Step 1: Infer canonical schema once
canonical = infer_canonical_schema(
df,
table_name='events',
dataset_name='analytics',
partition_columns=['event_date'],
cluster_columns=['user_id']
)
# Step 2: Render to any platform
for platform in ['bigquery', 'snowflake', 'redshift']:
renderer = RendererFactory.get_renderer(platform, canonical)
ddl = renderer.to_ddl()
print(f"{platform.upper()} DDL:")
print(ddl)
print()
Optimized DDL with Clustering & Partitioning
from schema_mapper.generators_enhanced import get_enhanced_ddl_generator
from schema_mapper.ddl_mappings import DDLOptions, ClusteringConfig, PartitionConfig, PartitionType
# BigQuery: Partitioned by date, clustered by user_id
generator = get_enhanced_ddl_generator('bigquery')
options = DDLOptions(
partitioning=PartitionConfig(
column='event_date',
partition_type=PartitionType.TIME,
expiration_days=365
),
clustering=ClusteringConfig(columns=['user_id', 'event_type'])
)
# Generate optimized DDL
ddl = generator.generate(
schema=schema,
table_name='events',
dataset_name='analytics',
project_id='my-project',
ddl_options=options
)
# Result: CREATE TABLE with PARTITION BY and CLUSTER BY